Android: Camera相机开发详解(上) —— 知识储备
Java设计模式透析
Android图片加载框架最全解析
Glide使用总结
首先,添加依赖
implementation 'com.github.bumptech.glide:glide:4.11.0'
之后添加访问网络权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
一、常用的方法
1、加载图片到imageView
Glide.with(this).load(url).into(imageView);
2、加载带有占位图
Glide.with(this).load(url).placeholder(R.drawable.loading).into(imageView);
3、加载指定大小的图片
Glide.with(this)
.load(url)
.placeholder(R.drawable.loading)
.override(100, 100)//指定图片大小
.into(imageView);
OkSocket与Android的简单使用
OkSocket简介
- OkSocket是一款基于阻塞式传统Socket的一款Socket客户端整体解决方案.你可以使用它进行基于Tcp协议的Socket通讯.就是我们所说的长连接.
- 对通讯协议几乎无限制,可以使用PB,可以使用JSON,可以使用XML.只要可以序列化成Byte数组的对象都可以传输.
- 兼容所有语言写的Socket服务端,解决了Tcp通讯中头疼的粘包拆包问题,断线重连问题,心跳保持问题,分片发送,重定向连接等问题.
- 针对 手机 < – > 服务器 , 手机< – > 手机 间都可以进行tcp通讯,手机间通讯俗称点对点通讯,可以很好的支持.
- OkSocket还支持单工和全双工通讯.适配各种复杂业务场景.分为 客户端(OkSocketClient) 服务端(OkSocketServer)具体的继承和依赖方法在下面.
- 如果需要看demo程序,可以去https://github.com/xuuhaoo/OkSocket地址进行clone.之后直接run起来就可以了.Demo会自动和OkSocket编写的EchoServer进行连接通讯,让使用者更好地了解使用方法
- OkSocket旨在让更多不熟悉socket和tcp协议的朋友可以专注于业务开发而不是底层协议的开发和学习.
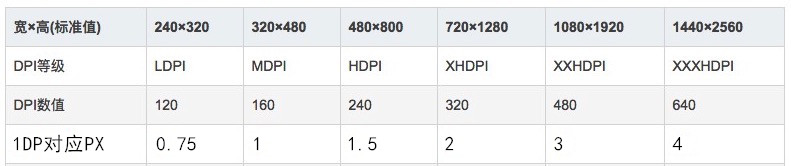
Android中分辨率,DPI,DP与PX对应关系
屏幕密度(DPI)
就是每英寸的像素点数,数值越高当然显示越清晰,通常 与“正常”或“高”密度屏幕相比,“低”密度屏幕在给定物理区域的像素较少。
密度无关像素 (dp)
在定义 UI 布局时应使用的虚拟像素单位,用于以密度无关方式表示布局维度 或位置。
密度无关像素等于 160 dpi 屏幕上的一个物理像素,这是 系统为“中”密度屏幕假设的基线密度。在运行时,系统 根据使用中屏幕的实际密度按需要以透明方式处理 dp 单位的任何缩放 。dp 单位转换为屏幕像素很简单: px = dp * (dpi / 160)。 例如,在 240 dpi 屏幕上,1 dp 等于 1.5 物理像素。在定义应用的 UI 时应始终使用 dp 单位 ,以确保在不同密度的屏幕上正常显示 UI。
六种通用的密度: ldpi(低)~120dpi mdpi(中)~160dpi hdpi(高)~240dpi xhdpi(超高)~320dpi xxhdpi(超超高)~480dpi xxxhdpi(超超超高)~640dpi
dp、dpi与px的换算
Android样式开发之你应该学会的layer-list!
节选自:Android样式开发之你应该学会的layer-list!
我们在前面已经讲过了shape和selector,可以说它们在Android的界面设计开发当中用的非常多,对控件的美化至关重要!
第一:是什么?
而今天我们要学习的layer-list可以进一步扩展对shape和selector的使用,对layer-list可以这样简单的来理解,使用它可以将多个图片叠加起来,可以将用shape和selector实现的效果叠加起来。比如我们可以使用shape绘制一个形状,我们这里以直观的矩形为例吧!如下,是我们使用shape绘制的一个矩形。 继续阅读Android样式开发之你应该学会的layer-list!
Android样式开发之selector使用
selector是什么?
selector是选择器的意思,从字面上理解应该是给我们提供可选择对象,那么在Android开发当中是什么呢?我们上一篇讲到Android样式开发中的shape,我们知道shape可以为控件设置背景,但是如果遇到这样的需求我们该怎么办呢?–对于一个button,我们点击的时候是一个图片,默认的时候是另一张图片。这样的话用shape似乎无法实现,因为shape无法控制一个控件状态的改变,对,我们要记住状态两个字,因为selector就是为多种控件在不同状态下显示不同的效果,这里的状态包括,被点击,被按压,被触摸以及被选中等状态,当一个按钮被点击和没有被点击的时候,我们可以通过selector让其显示不同的背景或者字体颜色等。
GSONFormat的简单使用
节选自:GSONFormat的简单使用
GsonFormat 插件的用法
在Android Studio中,可以利用 GsonFormat插件,快速创建符合 Gson要求的 javaBean 。GSONFormat地址:https://github.com/zzz40500/GsonFormat
使用过程
小tip:应该直接把从接口拿到的数据粘贴,避免 api 文档格式问题带来的各种不必要的 bug
Android Studio 常用快捷键
1.全局搜索类:Ctrl + N
2.全局搜索文件:Ctrl + Shift + N
3.搜索字符串:Ctrl + F
4.全局搜索字符串:Ctrl + Shift + F
5.快速生成构造函数,Get、Set方法等:Alt + Insert
6.编辑位置回退/前进:Ctrl + Alt + 向左箭头/向右箭头
7.左右切换代码视图:Alt + 向左箭头/向右箭头
8.自动导入包:Ctrl + Alt + O
9.格式化代码:Ctrl + Alt + L
10.方法参数提示:Ctrl + P
11.用“try / catch”等包围代码:Ctrl + Alt + T
12.跳转到声明位置(PS:也可以跳转到使用位置):Ctrl + B ,Ctrl + 鼠标左键
13.跳转到实现位置:Ctrl + Alt + B
14.编辑界面横向滚动:Shift + 鼠标滚动
15.跳转到父类方法:Ctrl + U
参考链接: