前言
本文将介绍在Android Studio中,android单元测试的介绍和实现。相关代码托管在github上的AndroidJunitDemo中,涉及到的用例代码收集于google官方提供的测试用例android-testing,同时进行了简化和修改。你可以从该demo中学习单元测试简单的使用,在工程中,包含两个模块,一个实现计算器功能的CalculationActivity,另外一个是PersonlInfoActivity,可以编辑姓名,邮箱和生日等信息,并保存到SharePreferences中,同时提供了两个模块的单元测试。
单元测试
关于单元测试,在维基百科中,给出了如下定义:
在计算机编程中,单元测试(英语:Unit Testing)又称为模块测试, 是针对程序模块(软件设计的最小单位)来进行正确性检验的测试工作。程序单元是应用的最小可测试部件。在过程化编程中,一个单元就是单个程序、函数、过程等;对于面向对象编程,最小单元就是方法,包括基类(超类)、抽象类、或者派生类(子类)中的方法。
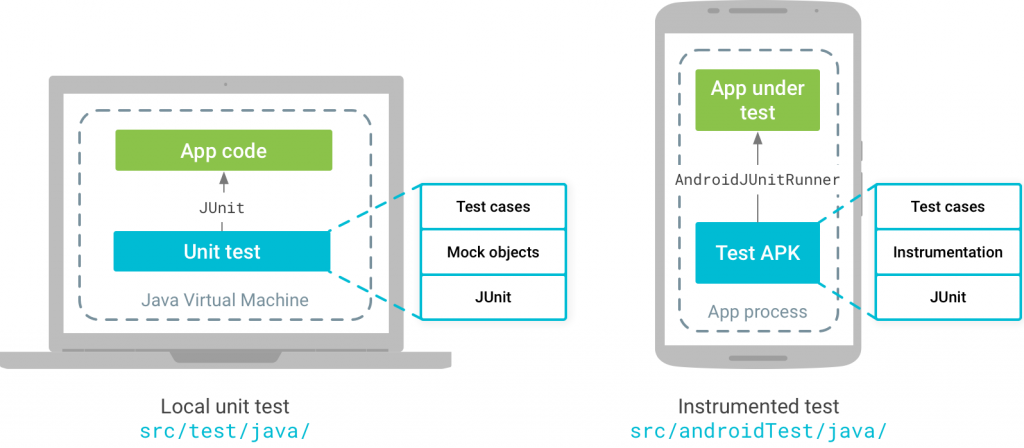
android中的单元测试基于JUnit,可分为本地测试和instrumented测试,在项目中对应
- module-name/src/test/java/.
该目录下的代码运行在本地JVM上,其优点是速度快,不需要设备或模拟器的支持,但是无法直接运行含有android系统API引用的测试代码。 - module-name/src/androidTest/java/.
该目录下的测试代码需要运行在android设备或模拟器下面,因此可以使用android系统的API,速度较慢。
以上分别执行在JUnit和AndroidJUnitRunner的测试运行环境,两者主要的区别在于是否需要android系统API的依赖。
在实际开发过程中,我们应该尽量用JUnit实现本地JVM的单元测试,而项目中的代码大致可分为以下三类:
- 1.强依赖关系,如在Activity,Service等组件中的方法,其特点是大部分为private方法,并且与其生命周期相关,无法直接进行单元测试,可以进行Ecspreso等UI测试。
- 2.部分依赖,代码实现依赖注入,该类需要依赖Context等android对象的依赖,可以通过Mock或其它第三方框架实现JUnit单元测试或使用androidJunitRunner进行单元测试。
- 3.纯java代码,不存在对android库的依赖,可以进行JUnit单元测试